When considering a career in nursing, one might wonder how much time they will need to dedicate to education. Interestingly, the length of nursing school can vary greatly, depending on the type of program pursued. Some might be surprised to learn that an accelerated program can be completed in as little as 12 to 18 months, a stark contrast to the typical four-year bachelor’s degree.
The duration of nursing school is influenced by multiple factors including program type and level of education. Historically, nursing education has evolved, offering a diverse range of pathways such as Associate of Science in Nursing (ASN) degrees, which generally take two years. Statistical data reflects that approximately 35% of nursing students opt for these shorter pathways, making it a flexible option for those eager to enter the workforce quickly.
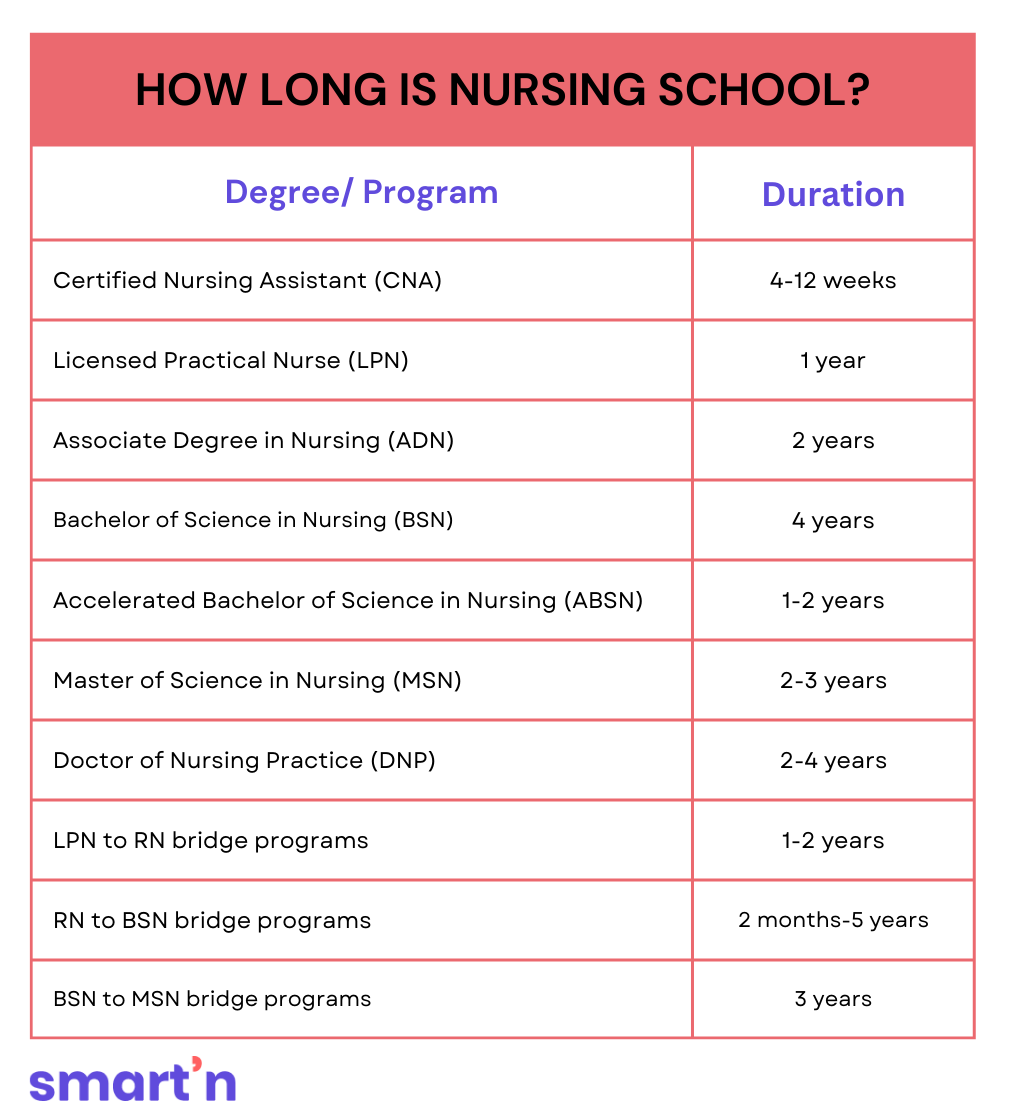
The duration of nursing school varies depending on the chosen program. An Associate Degree in Nursing typically takes two years, while a Bachelor of Science in Nursing requires approximately four years. Accelerated programs offer completion in 12 to 18 months for those with prior degrees, tailored to different career goals and timelines. ❤❤
How long is Nursing School?
Nursing school duration varies depending on the pathway chosen. Many students start with an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), which usually takes about two years to complete. For those pursuing a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), the program typically lasts four years. Interestingly, there are accelerated programs for those who already hold a degree in another field. These can often be completed in 12 to 18 months.
Each program has its unique benefits and timelines. An ADN offers entry into the nursing field more quickly, while a BSN provides broader knowledge and skills. Many hospitals prefer hiring nurses with a BSN due to their comprehensive training. Some programs even offer dual options, allowing students to transition from an ADN to a BSN. This flexibility helps tailor education to career goals and needs.
Accelerated nursing programs offer an exciting option for those looking to change careers. They condense the curriculum into a shorter time with intense and focused coursework. This path is best suited for students who can dedicate full-time study. Despite the rigorous pace, it provides a fast track into the nursing profession. Many students find it worthwhile for the quick transition.
The time span for nursing education can also be affected by state requirements and educational institutions. Some states have mandatory courses that can extend the program length. Students should research specific requirements in their area of interest. Additionally, part-time study options exist but will extend the completion time. Overall, understanding and planning are key to navigating the nursing education landscape efficiently.
Factors Influencing Duration
Several factors determine how long it takes to complete nursing school. The type of program selected plays a significant role. For instance, an Associates Degree in Nursing (ADN) generally requires less time than a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). Personal life circumstances can also impact the duration. Balancing family, work, and studies may extend the timeline for some students.
Program format is another important factor. Full-time programs allow students to complete their studies in the shortest time. Part-time programs provide flexibility but take longer. This option is suitable for those who need to manage other commitments. Deciding between these formats can affect how quickly you enter the nursing profession.
The educational background of students influences the length of nursing education too. Those with previous healthcare experience might find some coursework familiar and easier. Programs may offer credit for past relevant studies or experience. This can lessen the required course load and reduce completion time. Advanced placement options can further expedite progress.
State-specific requirements can also add to the time needed in nursing school. Each state might have unique prerequisites or mandated courses. It’s essential to understand these regulations before enrolling in a program. Researching and planning accordingly helps students avoid unexpected delays. By knowing these factors, students can make informed decisions about their educational pathways.
Different Pathways to Become a Nurse
Becoming a nurse can be achieved through various educational pathways. One common route is obtaining an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN). This program typically takes two years and is offered at many community colleges. It’s a popular choice for those who want to start working sooner. Graduates can then pursue further education while gaining experience.
An alternative is the Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program. A BSN takes about four years to complete at universities. This degree provides a broader education in nursing and healthcare. It opens up more opportunities for advancement and specialization. Many healthcare facilities prefer candidates with a BSN for their comprehensive training.
For those with a non-nursing bachelor’s degree, accelerated nursing programs offer a quick entry into the field. These programs can be completed in just 12 to 18 months. They are intensive and require full-time study. This rapid pace is appealing for career changers eager to enter nursing. It allows them to leverage their previous education effectively.
There are also diploma programs offered by hospitals with nursing schools. These programs often take about two to three years and focus heavily on clinical skills. While not as common as they once were, they still provide a direct path into nursing. Graduates may find it beneficial to further their education later. Each pathway has its unique features, offering flexibility to match individual needs and goals.
Time Frame for Each Nursing Program
The journey to becoming a nurse can vary significantly based on the program chosen. An Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) generally requires two years to complete. Many students opt for this path due to its shorter duration. It provides a quick launch into the nursing industry. However, some choose to continue their education beyond this degree.
Pursuing a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) typically takes about four years. This program is more comprehensive and includes a wider range of topics. Besides core nursing skills, students study management, research, and community health. A BSN degree often opens doors to more advanced positions. Many healthcare facilities increasingly prefer BSN candidates.
For those who already hold a bachelor’s degree in another field, an accelerated BSN program might be the best choice. These programs can be completed in 12 to 18 months, significantly faster than traditional programs. They are intensive, requiring dedication and full-time effort. Despite the rigor, they offer a swift shift into nursing careers. This option is particularly attractive for career changers.
Nursing schools affiliated with hospitals sometimes still offer diploma programs. Typically, these programs take about two to three years. They focus heavily on hands-on clinical skills training. Although less common today, some students still prefer this direct approach. Diploma graduates might pursue further education for additional credentials.
Lastly, there’s the option of pursuing a Master’s degree in Nursing for those looking at advanced practice roles. This can take an additional two years of study after completing a BSN. Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs) often specialize further. This pathway allows experienced nurses to gain deeper expertise in areas like midwifery or nurse practitioners. It’s a path chosen by those aiming for higher responsibilities and autonomy in patient care. ❤❤❤
Accelerated Nursing Programs
Accelerated nursing programs are designed for students who already hold a bachelor's degree in another field. These programs offer a fast-paced way to earn a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). Typically, they can be completed in just 12 to 18 months. Students focus intensely on nursing courses without general education classes. This structure helps speed up the path to becoming a registered nurse.
The curriculum in accelerated programs is comprehensive and challenging. Students must be prepared for long hours of study and fieldwork. Courses cover essential nursing concepts, clinical practices, and patient care. Labs and clinical rotations form a core part of the training. These hands-on experiences are crucial for gaining practical skills.
Many candidates are drawn to these programs due to their quick turnaround. They cater especially to those eager to shift careers into healthcare rapidly. The rigorous nature fits well for highly motivated individuals. Upon completion, graduates are equipped to take the NCLEX-RN exam. This exam is necessary to become a licensed nurse.
There are some advantages of choosing an accelerated program. First, it saves time by leveraging existing degrees. Second, it can be cost-effective due to the shorter duration. These benefits make it a popular choice for many students. Additionally, graduates often find rewarding career prospects in various healthcare settings.
However, the intensity of these programs may not be suited for everyone. Balancing life and studies requires strong time management skills. It's also crucial to have a support system in place. Family and friends can provide significant help during this demanding period. Considering these factors can lead to a successful experience in accelerated nursing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Nursing careers offer various pathways and opportunities, making them highly popular. Here, we answer some common questions about pursuing a career in nursing.
1. What are the prerequisites for enrolling in a nursing program?
Most nursing programs require applicants to have a high school diploma or GED. Additionally, coursework in biology, chemistry, and math is often needed. Some programs might ask for a certain GPA or entrance exam scores like the TEAS. These prerequisites ensure students have a strong foundation for nursing studies.
Having relevant volunteer or healthcare experience can also boost your application. Engaging with healthcare settings provides practical insights. It helps prospective students decide if nursing is the right fit for them. Many programs value this exposure highly and consider it during admissions decisions.
2. Can I work while attending nursing school?
Balancing work and nursing school is possible but requires careful time management. Full-time programs, especially accelerated ones, are demanding and may leave little room for employment. However, many students work part-time or choose flexible jobs to accommodate study schedules.
Online courses or part-time programs can offer more flexibility. They allow students to better manage their time between work and studies. Nursing education involves clinical rotations, which also require time. Planning ahead and communicating with employers about your commitments can help balance both responsibilities.
3. Are there online nursing programs available?
Yes, many nursing programs offer online courses, particularly for theoretical components. Online programs provide flexibility, making them ideal for those balancing other commitments. However, practical skills and clinical experience must be completed in-person at designated healthcare facilities.
Hybrid programs blend online learning with local clinical placements. This format allows students to study remotely while gaining hands-on experience. Accredited online programs ensure graduates are well-prepared and eligible for licensure exams, just like traditional program graduates.
4. What is the difference between an RN and an LPN?
Registered Nurses (RNs) and Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) differ in education, responsibilities, and job opportunities. RNs typically complete a two to four-year degree, while LPNs have shorter, diploma-based programs. The scope of practice for RNs is broader, allowing them to administer medication, create care plans, and supervise LPNs.
LPNs focus more on basic patient care under RN supervision. They assist with daily activities, monitor patients, and report changes to RNs. Advancement opportunities for LPNs are limited compared to RNs. Education and certification level influence the roles they can hold and the career paths available to them.
5. Is it worth pursuing a career in nursing?
Nursing is a rewarding career with diverse opportunities. Nurses are essential in healthcare, making a real impact on patient lives. The field offers various specializations and the chance to work in different environments, from hospitals to community clinics.
Job security is high, as the demand for skilled nurses continues to grow. Competitive salaries and benefits make it an attractive career choice. Many find fulfillment in helping others and contributing to the community. Considering the personal and professional rewards, many believe a nursing career is undoubtedly worth it.